Viral Hepatitis,Types
Hepatitis
How is viral hepatitis defined?
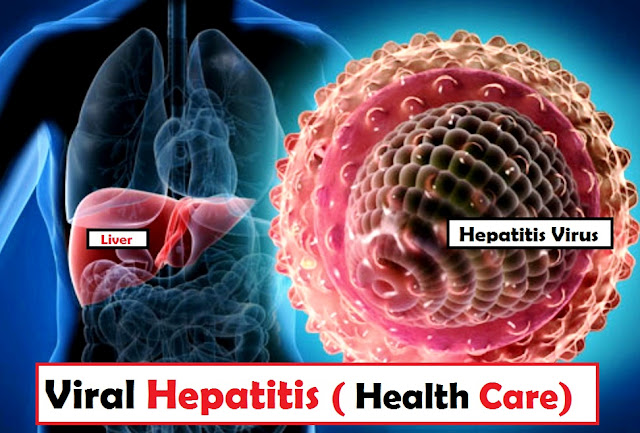
An illness called viral hepatitis damages and inflames the liver. Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E are only a few of the viruses that may cause it. Hepatitis A and E viruses can result in severe illnesses. Chronic and acute infections can be brought on by the hepatitis B, C, and D viruses.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A only results in an acute infection, which usually resolves on its own after a few weeks. Contact with the faeces of an infected individual allows the hepatitis A virus to spread. By receiving the hepatitis A vaccination, you can safeguard yourself.
Hepatitis B
Acute or persistent infection can be brought on by hepatitis B. If you are expecting a child or have a high risk of contracting hepatitis B, your doctor could suggest being tested. Getting the hepatitis B vaccination will protect you against hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C
Acute or chronic infection can be brought on by hepatitis C. Typically, doctors recommend a single hepatitis C screening for all people aged 18 to 79. Liver damage can be stopped with early detection and treatment.
Hepatitis D
Because it may only infect you if you already have an infection with the hepatitis B virus, the hepatitis D virus is rare. When you have both hepatitis D and hepatitis B at the same time, you have a coinfection. If you currently have chronic hepatitis B and subsequently get hepatitis D, this is known as a "superinfection."
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E is often an acute illness that resolves on its own within a few weeks without medical intervention. Drinking water tainted by an infected person's faeces can spread some forms of the hepatitis E virus. Wild wildlife or undercooked meat can spread other varieties.
Viral Hepatitis
An illness called viral hepatitis damages and inflames the liver. When bodily tissues are harmed or diseased, inflammation—which is swelling—occurs. Organ damage is a risk from inflammation. Hepatitis viruses such as hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E have all been identified by researchers as the primary causes of hepatitis.
Food or water that has been tainted by the faeces of an infected individual can be a source of transmission for both hepatitis A and E. Eating undercooked pork, deer, or seafood can potentially transmit the hepatitis E virus to people.
Through contact with blood from an infected individual, hepatitis B, C, and D are transmitted. Other bodily fluids might potentially be contaminated by hepatitis B and D. Many different scenarios exist, such as sharing syringes used to inject drugs or having unprotected .
Only acute, or short-term, infections are normally brought on by the hepatitis A and E viruses. In an acute infection, the virus is defeated by your body's ability to fight it off.
Hepatitis B, C, and D viruses can result in both acute and chronic illnesses.
When the hepatitis virus persists and your body is unable to eliminate it, you
get chronic hepatitis. Cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer are some of
the problems that can result from chronic hepatitis. Your risk of having these
problems can be avoided or reduced with early detection and treatment of
chronic hepatitis.
Non-A-E hepatitis or hepatitis X are terms used by doctors when they are unable to determine the source of a patient's hepatitis. According to experts, unidentified viruses in addition to hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E may be to blame for certain hepatitis cases. These viruses are being identified by researchers.
Non-A-E hepatitis is often acute, although it can also develop into a chronic condition.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A: What is it?
A viral illness called hepatitis A damages and inflames the liver. Swelling caused by inflammation happens when bodily tissues are damaged or diseased. Organs can be harmed by inflammation.
Invading viruses enter healthy cells in your body. Many viruses can infect people and transmit such illnesses. Typically, the hepatitis A virus spreads through contact with food or drink that has been tainted by the faeces of an infected person.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B: what is it?
A viral illness called hepatitis B damages and inflames the liver. Swelling caused by inflammation happens when bodily tissues are damaged or diseased. Organs can be harmed by inflammation.
Invading viruses enter healthy cells in your body. Numerous viruses may infect people and transmit such illnesses. Contact with blood, semen, or other bodily fluids from an infected individual can spread the hepatitis B virus.
You may take precautions against hepatitis B, such as receiving the hepatitis B vaccination. If you have hepatitis B, you can take precautions to prevent others from getting the disease.
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C: What is it?
A viral illness called hepatitis C damages and inflames the liver. Swelling caused by inflammation happens when bodily tissues are damaged or diseased. Organs can be harmed by inflammation.
Invading viruses enter healthy cells in your body. Many viruses can infect people and transmit such illnesses. Contact with the blood of an infected individual is how the hepatitis C virus spreads.
An acute or persistent infection can be brought on by hepatitis C.
Despite the lack of a hepatitis C vaccination, there are things you can do to safeguard yourself. Discuss treatment options with your doctor if you have hepatitis C. Most hepatitis C cases may be cured with medication.
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D: What is it?
A viral illness called hepatitis D damages and inflames the liver. Swelling caused by inflammation happens when bodily tissues are damaged or diseased. Organs can be harmed by inflammation.
Invading viruses enter healthy cells in your body. Numerous viruses may infect people and transmit such illnesses.
Because it may only infect you if you already have an infection with the hepatitis B virus, the hepatitis D virus is rare. Hepatitis D is a twofold infection in this way. By having the hepatitis B vaccination, you may protect yourself against hepatitis B as well as hepatitis D.
The same way that hepatitis B spreads, hepatitis D spreads through contact with the blood or other bodily fluids of an infected individual.
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E: What is it?
A viral illness called hepatitis E damages and inflames the liver. Swelling caused by inflammation happens when bodily tissues are damaged or diseased. Organs can be harmed by inflammation.
Invading viruses enter healthy cells in your body. Different strains of the hepatitis E virus transmit in various ways.
Taking polluted water to consume can spread certain kinds of bacteria. These kinds are more frequent in developing nations, such as the Middle East, Africa, Asia, and areas of Central America.
Eating undercooked pork or wild game, including deer, can transmit other
strains. In wealthy nations like the United States, Australia, Japan, and some
regions of Europe and East Asia, these kinds are increasingly prevalent.