Human Heart Circulatory System-Works- Diseases
Heart
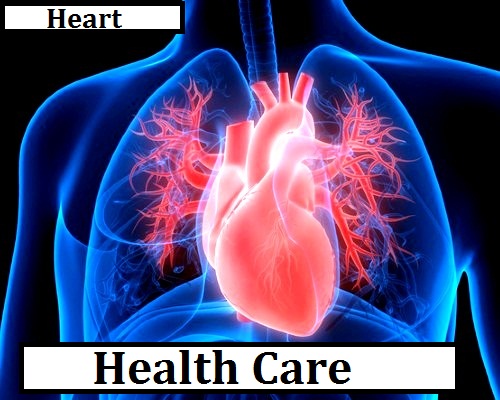
Your heart is the pump its muscular organ about the size of your fist and is located slightly left of center in your chest. Your heart is divided into the right and left side the division protects oxygen-rich blood from mixing which oxygen poor blood together your heart and blood vessels comprise your body's cardiovascular system pumps blood and oxygen throughout it.
5 quarts of blood
every minute
In fact your heart pumps about quarts of blood every minute and it beats about one hundred thousand times in one day that’s about thirty five millions times in a year.
Oxygen poor blood blue blood return to the heart after circulating through your body.
Heart Atriums
The right side of heart composed of right atrium and ventricle collects and pumps the blood to the lungs through the pulmonary arteries the lungs refresh the blood with a new supply of oxygen making in turn end oxygen-rich blood red blood then enters the left side of heart composed of the left and ventricle and is pumped through the aorta to the body supply tissues with the oxygen four valves within your heart keep your blood moving the right way.
Tricuspid mitral
pulmonary and aortic valves
Tricuspid mitral pulmonary and aortic valves work like gates on a fence they open only one way and only when pushed on each valve open and closes once per heartbeat or about once every second.
Systole
and Diastole
A beating heart contracts and relaxes contraction is called systole
Relaxing is called diastole
during systole your ventricles contract forcing blood into the vessels going to your lungs and body much like ketchup being forced out a squeeze bottle the right ventricle contracts a little bit before the left ventricle does your ventricles then relax during diastole and are the filled with blood coming from the upper chambers the left and right atria then the cycle starts over again.
Your heart is nourished by blood too blood vessels called coronary arteries extend over the surface of your heart and branch into smaller capillaries just the network of blood vessels that feed your heart with oxygen-rich blood.
Your heart also has a electrical wiring which keeps it beating electrical impulses begin high in the right atrium and travel through specialized pathways to the ventricles delivering the signals to pump the conduction system keep your heart beating in a coordinated normal rhythm which in turn keep blood circulating in continuous exchange of oxygen-rich blood with oxygen poor blood is what keeps your life.
Blood flow through the heart
VEINS – BLOOD VESSELS CONTAINING BLOOD FLOWING TO THE HEART
Veins are blood vessels containing blood flowing the heart, while arteries have blood flowing from the heart.
DEOXYGENATED
BLOOD
The Blue representatives of blood vessels containing deoxygenate blood
OXYGENATED
BLOOD
Fresh blood from the lungs that has been oxygenated is in the red blood cells.
CONDUCTION OF THE
HEART
When special cells called pacemakers cells generate electrical signals inside your heart the heart muscle cells called myocytes contract as group.
CIRCULATION &
THE HEART
Your heart is divides into left and right halves which works together like a dual pump on the right side of your heart deoxygenated blood from body’s tissues flows through large veins called the superior and inferior vena cava into your right atrium, the blood moves into your right ventricle which contracts and sends blood out of your heart to the your lungs to gather oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide on the left side of your heart oxygen-rich blood from your lungs flows through your pulmonary veins into your left atrium the blood then moves into your left ventricle, which beats and pushes blood down the aorta from your heart to nourish your cells and tissues.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS
Medicine book let’s jump straight in so first let’s talk about atherosclerosis is through basically means soft or porridge-like sclerosis is hardening and atherosclerosis is really a combination of a through m’as which have fatty deposit in artery wall and sclerosis which is the process of hardening of stiffening of the blood vessels wall.
Atherosclerosis affects the medium and large arteries in the body and the its caused by chronic inflammation and activation of the immune system in the artery wall so this causes deposits of lipids in the artery wall followed by the development of fibrous atheromatous plaques caused a few different problems firstly they cause stiffening of the artery wall which leads to hypertension raised about blood pressure this is caused by the strain on the heart trying to pump blood against an artery wall what wont expand with the extra pressure so its pumps against the extra resistance causes higher blood pressure. the second problem is stenosis so this is narrowing because of the plaques of the space that the blood flow through in the blood vessel this would cause reduced Blood flow in diseases such peripheral vascular disease and angina. The third problem is plaque rapture and this is where the plaque breaks off and gives of something called thrombus that travels down the vessels and block a distal part of the blood vessel leading to ischemia and this is the main cause of acute coronary syndrome of heart attacks.
Heart
problems
A heart attack, often referred to as a myocardial infarction, can occur when a segment of the heart muscle isn't receiving enough blood.
The longer it goes without treatment to increase blood flow, the more damage is done to the heart muscle.
Heart attacks are mostly caused by coronary artery disease (CAD). An extremely strong spasm, or sudden contraction, of a coronary artery, is a less common cause that might prevent blood flow to the heart muscle.
Angina
or soreness in the chest might indicate a heart attack.
Left- or center-sided chest discomfort that lasts for more than a few minutes or that comes and goes is the most common sign of a heart attack. The sensation may feel like a squeezing, fullness, or pressure that is uncomfortable.
• feeling weak, faint, or woozy. You may also begin to perspire profusely.
• Aches or pains in the jaw, neck, or back
• One or both shoulders or arms might hurt or feel unpleasant.
•breathing issues Chest discomfort and breathlessness usually co-occur, however chest pain can begin before it as well.